In the ever-evolving landscape of data storage, the choice of tape drives plays a pivotal role in optimizing operational efficiency and reliability. One key decision to make is whether to opt for a Full Height (FH) or Half Height (HH) LTO-9 tape drive. This article aims to shed light on the advantages of employing Full Height drives, exploring their unique features and benefits that make them particularly suitable for specific use cases.
Full-Height LTO-9 tape drives boast several noteworthy advantages over their Half Height counterparts, making them the preferred choice for high-duty cycle environments and scenarios involving frequent access to files stored in multiple locations on the same cartridge. These drives also excel in applications where loading and unloading numerous cartridges are routine, especially in archive use cases.

Full Height Drives features that makes it a better choice
Larger Motors for Increased Reliability
The FH drive’s spacious design accommodates larger motors, enhancing mechanical reliability. Despite similar reliability ratings, the larger motors operate at a lower percentage of the designed maximum load, contributing to overall tape drive durability.
Faster Media Movement and Acceleration
FH drives exhibit faster media movement, crucial for scenarios involving random file access. Additionally, their superior acceleration capabilities reduce the time taken for back-hitching cycles, providing a performance advantage in environments where back-hitching is common.
Dual Porting
FH drives feature dual ports, providing redundancy and failover protection. This is essential for maintaining tape drive operations in the face of network and server disruptions, making FH drives ideal for environments with limited tape libraries and drives.
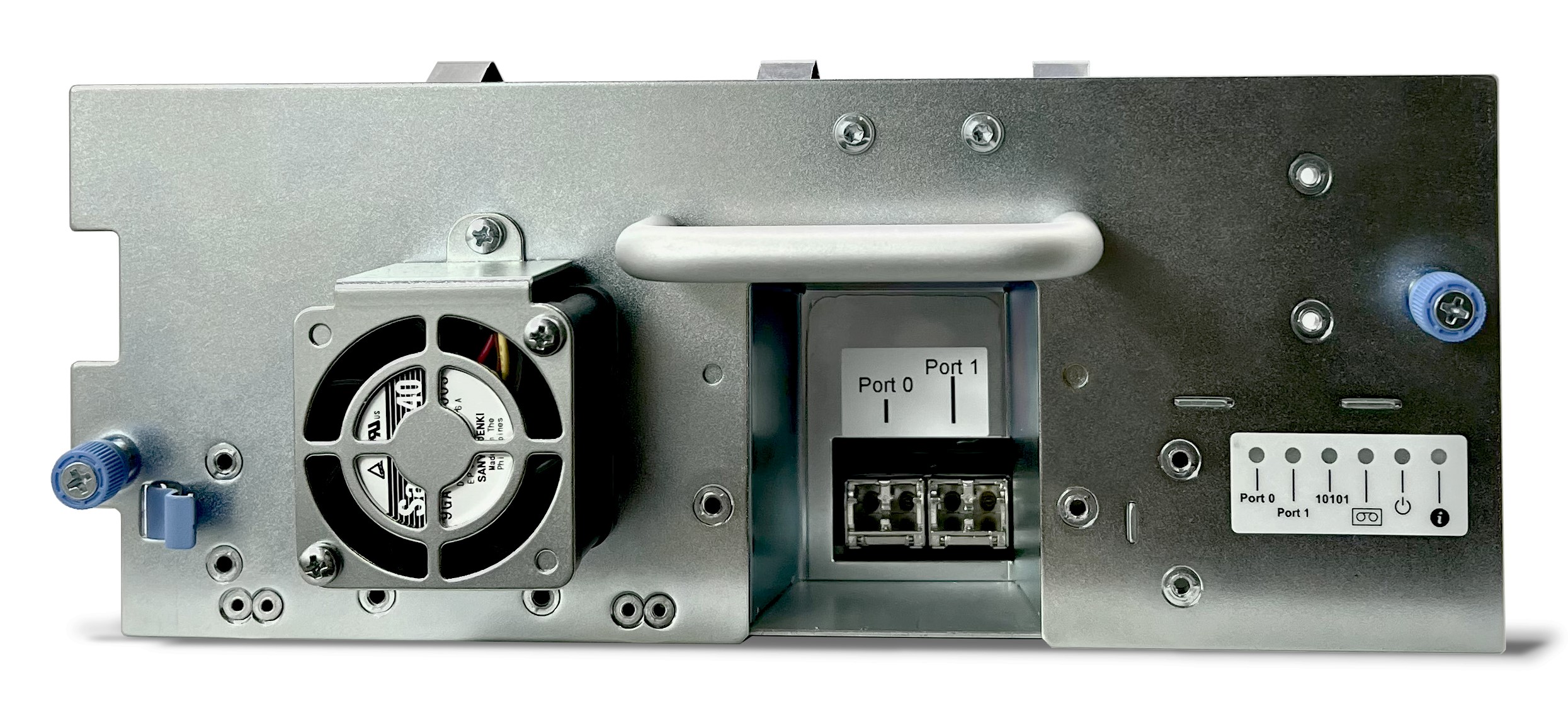

Greater Immunity to Shock and Vibration
The FH drive’s aluminum base plate offers increased immunity to shock and vibration, surpassing the specifications of HH drives. This robust design ensures optimal performance in challenging conditions.
Higher Cartridge Insertion Force Tolerance
FH LTO-9 drives can handle significantly greater insertion force, a critical factor in automated tape libraries with high load/unload cycles. The FH mechanism’s robustness is especially advantageous in archive use cases.
Higher Performance
FH drives exhibit higher throughput compared to HH drives, with a widening performance gap. The combination of larger motors and stable mechanical assemblies positions FH drives as a future-proof choice for sustained high performance.
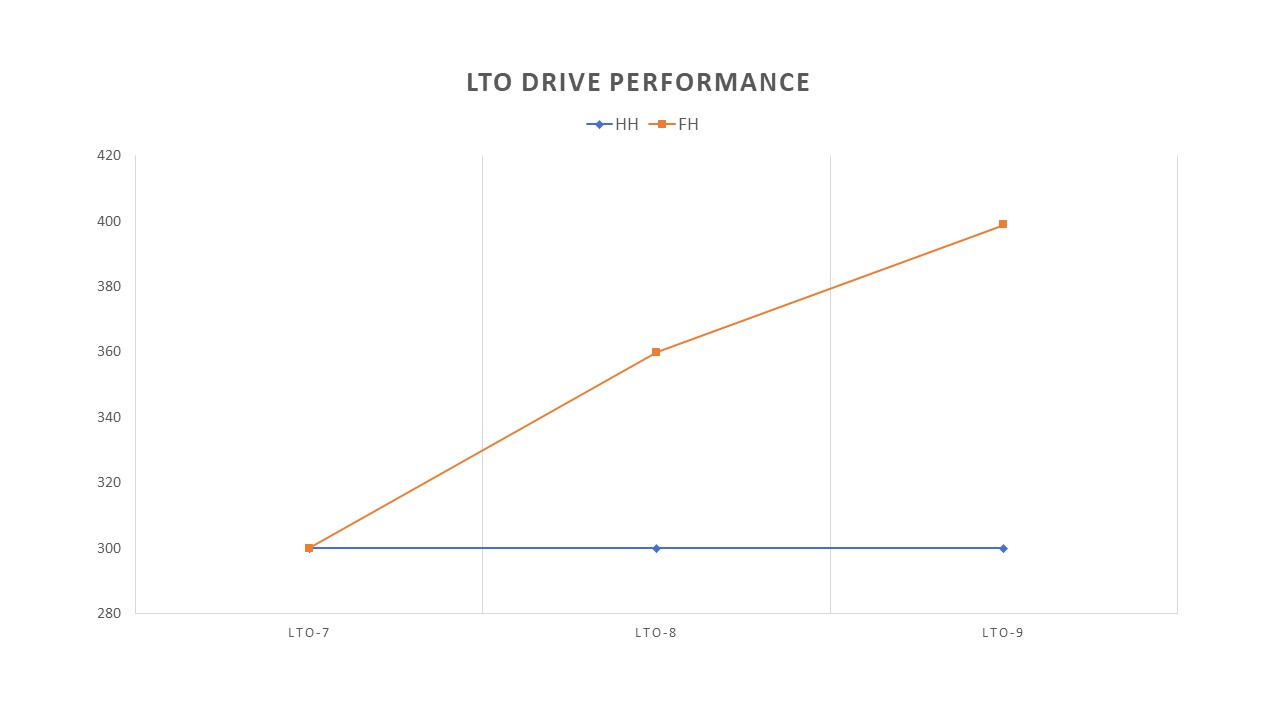
While both FH and HH versions share common characteristics, the distinctive features of Full Height LTO-9 tape drives make them the superior choice for demanding environments and specific use cases. The advantages in reliability, performance, and durability position FH drives as the preferred solution, particularly in enterprise settings where efficiency and speed are paramount.
Note: FH drive should be installed at the bottom of the NEOxl 40.
Back Hitching Definition
“Back hitching” is when a tape drive adjusts to slower data transfer from the host server. If the host’s data speed doesn’t match the drive’s capabilities, the drive initially slows down using its native speed matching. If the data rates fall below a set threshold, the drive temporarily stops the tape. When the data stream resumes, the drive performs a quick backward movement and then resumes normal operation. This process ensures synchronization between the tape drive and slower data transfer from the host server, preventing interruptions in data flow.
Note
When considering the choice between FH and HH drives, it’s essential to evaluate specific requirements and operational conditions, ensuring the selected drive aligns with the user’s goals for reliability, performance, and longevity in the rapidly evolving landscape of LTO technology.